rmNVMe IPRandom access by Multiple Users To NVMe SSD Simultaneously Without CPU!

rmNVMe-IP (Random Access & Multi User NVMe IP) is very high performance NVMe Host Controller which is highly optimized for high-IOPS random access applications. rmNVMe-IP supports multiple user interfaces, each user can simultaneously read/write to a single NVMe SSD at the same time. This IP is designed for the application that requires very random access performance such as real-time sensors data fusion and processing, OS file systems offloading and NVMe SSD tester. By pure hardware logic implementation, rmNVMe-IP is best in class in energy efficient, high performance and low FPGA resource usages for next generation applications.
| No CPU/DDR required Standard Type |
No PCIe Hard IP required | >500K IOPS random write access | Multi user simultaneously access | Random Access By Multiple Users |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Introduction Videos
 |
 |
Features
|
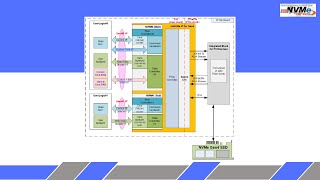
Block Diagram |
 * Click to show more detail |
Document download
Technical Documents
| Support Devices | Agilex™ F series | ||||
| IP core | Datasheet | Reference Design Document | Demo Instruction Document | Free Evaluation demo file | |
| rmNVMe-IP (Gen5) |
Rev1.0 | Rev1.0 | Rev1.0 | Agilex-I |  |
| rmNVMe-IP (Gen4) |
Rev1.0 | Rev1.0 | Rev1.1 | Agilex-F | |
Application Example
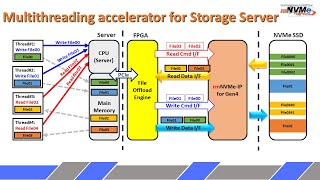
Multithreading for Database Server

The FPGA can be utilized as the offload engine for the database server to access storage, NVMe SSD. In large-scale systems, multiple threads frequently access the database, leading to a high volume of read and write requests being sent to the CPU. The write data, which is usually of a large size, is stored in the main memory. The FPGA platform's PCIe engine provides an interface that allows the offload engine to receive command requests from the CPU and directly access the data in the main memory with high performance.
The File Offload Engine sends read and write requests to the rmNVMe IP via the Read Command Interface and Write Command Interface, respectively. All write data is transferred via the Write Data Interface and stored in the NVMe SSD. The read data from the NVMe SSD is returned to the File Offload Engine via the Read Data Interface and finally, returned to the thread through the main memory.
By utilizing this hardware system, the database can be accessed with high performance while requiring less CPU resources.
Alliance Partner

Design Gateway Co., Ltd.
Head Office3-23-17 Naka-cho, Koganei, Tokyo, JAPAN
R&D
89/26 Amornpan 205 Tower1, 18th floor, Ratchadapisek7 (Nathong) Alley, Ratchadapisek Road, Din Daeng, Bangkok, 10400 THAILAND
AI Lab
Faculty of Engineering, Chulalongkorn University, 12th floor, Engineering 4 Building (Charoenvidsavakham), Phayathai Rd., Wang Mai, Pathumwan, Bangkok, 10330 THAILAND

